
Looking for a natural way to support your body’s excretion of spironolactone? Our innovative product is designed to aid in the elimination of this medication from your system.
Try our Spironolactone excretion supplement today and experience the benefits of a cleaner, healthier body!
Understanding Spironolactone Excretion
Spironolactone, a potassium-sparing diuretic, is primarily excreted in the urine. Its elimination from the body is crucial for maintaining electrolyte balance and managing conditions like hypertension and heart failure.
Mechanism of Excretion
Spironolactone undergoes extensive metabolism in the liver, forming active metabolites that are eventually eliminated via the kidneys. The drug and its metabolites are excreted both through glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion in the renal tubules.
Spironolactone’s excretion rate is influenced by factors such as renal function, age, and concomitant medications. In patients with impaired renal function, dosage adjustment may be necessary to prevent drug accumulation and potential toxicity.
- This section provides insights into the pharmacokinetics and dynamics of spironolactone excretion, highlighting the importance of proper dosing and monitoring in clinical practice.
- Understanding the mechanisms underlying spironolactone excretion is essential for healthcare providers to optimize treatment outcomes and minimize adverse effects.
Overview and Mechanism
Renal function plays a crucial role in the excretion of Spironolactone, a medication used to treat various conditions such as high blood pressure and heart failure. The renal system is responsible for filtering and eliminating waste products, including drugs, from the body. Spironolactone excretion primarily occurs through the kidneys, where the drug is metabolized and eventually eliminated in the urine.
Renal System Function
The kidneys are vital organs that help maintain fluid balance, regulate electrolytes, and filter waste products from the blood. The mechanisms involved in Spironolactone excretion rely on the intricate processes of glomerular filtration, tubular secretion, and reabsorption within the nephrons of the kidneys.
Importance of Renal Function
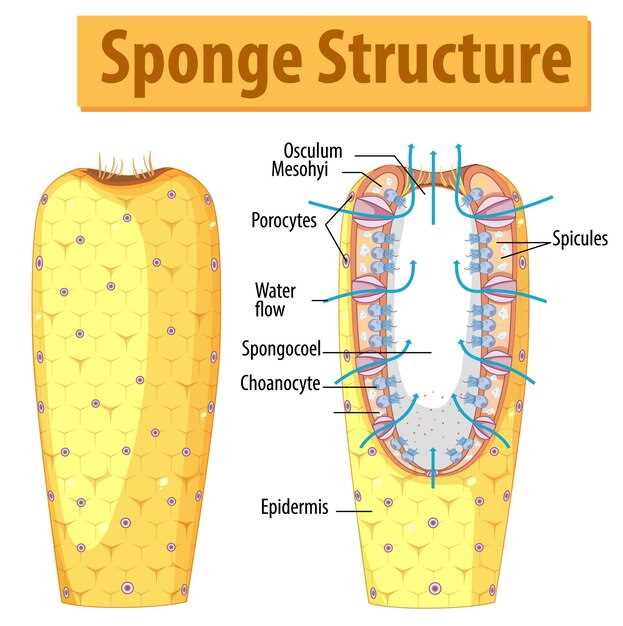
Renal function plays a crucial role in the excretion of spironolactone, a potassium-sparing diuretic used to treat conditions such as hypertension and heart failure. The kidneys are responsible for filtering and removing waste products, including medications, from the bloodstream.
Spironolactone is primarily excreted by the kidneys through urine. Therefore, maintaining proper renal function is essential for the effective elimination of spironolactone from the body. Impaired renal function can result in decreased excretion of spironolactone, leading to its accumulation in the body and potential adverse effects.
Patients with renal impairment require careful monitoring of spironolactone levels to prevent toxicity. Adjustments in dosage may be necessary based on the patient’s renal function to minimize the risk of adverse effects and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Healthcare providers should assess renal function and consider creatinine clearance when prescribing spironolactone to ensure safe and effective use of the medication. Regular monitoring of renal function parameters is essential to assess the excretion rate of spironolactone and adjust treatment accordingly.
Factors Affecting Excretion Rate
The excretion rate of Spironolactone can be influenced by a variety of factors that impact the pharmacokinetics and renal function. Understanding these factors is crucial for determining the appropriate dosage and monitoring the drug’s effectiveness.
| Factor | Effect on Excretion Rate |
|---|---|
| Renal Function | Impaired renal function can decrease the excretion rate of Spironolactone, leading to potential accumulation of the drug and increased risk of adverse effects. |
| pH of Urine | Changes in urine pH can affect the ionization of Spironolactone and its metabolites, influencing their excretion rates. |
| Drug Interactions | Co-administration of drugs that affect renal function or compete for renal excretion pathways can alter the excretion rate of Spironolactone. |
| Fluid and Electrolyte Balance | Dehydration or electrolyte imbalances can impact renal function and, consequently, the excretion rate of Spironolactone. |
| Metabolic Factors | Metabolic conditions such as liver disease can affect the metabolism of Spironolactone and its excretion rate. |
Monitoring these factors in patients receiving Spironolactone is essential to optimize therapy, prevent adverse effects, and ensure therapeutic efficacy.
Clinical Implications and Monitoring
Enhancing Spironolactone excretion is crucial in certain clinical conditions where excessive retention of potassium and sodium can lead to adverse effects. Monitoring the excretion rate of Spironolactone allows healthcare providers to optimize dosing regimens and ensure patient safety.
| Monitoring Parameters | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Potassium Levels | Weekly initially, then as indicated |
| Serum Creatinine | Baseline, then every 3-6 months |
| Renal Function Tests | Regularly as per clinical judgment |
| Electrolyte Panel | Regularly as per clinical judgment |
Clinical implications of inadequate Spironolactone excretion can include hyperkalemia, electrolyte imbalances, and potential renal impairment. Monitoring these parameters can help prevent adverse effects and optimize the therapeutic benefits of Spironolactone in patients with heart failure, hypertension, and edema.
Healthcare providers should educate patients on the importance of adherence to monitoring schedules and reporting any symptoms of electrolyte disturbances promptly. Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers and patients are essential to ensure the safe and effective use of Spironolactone.
Enhancing Spironolactone Excretion
Enhancing spironolactone excretion can be crucial in certain clinical scenarios where rapid elimination of the drug is desired. Several strategies can be employed to promote spironolactone excretion:
- Increased fluid intake: Adequate hydration can help increase urine output and promote the excretion of spironolactone.
- Alkalinization of urine: Alkalinizing the urine can enhance the elimination of spironolactone as it favors the conversion of spironolactone to its more water-soluble metabolite.
- Use of diuretics: Certain diuretics like thiazides can increase the excretion of spironolactone by affecting renal function and electrolyte balance.
- Monitoring electrolytes: Regular monitoring of electrolytes like potassium and sodium is essential when enhancing spironolactone excretion to prevent imbalances.
By employing these strategies, healthcare providers can optimize spironolactone excretion in patients when necessary, ensuring effective drug elimination and minimizing potential side effects.
Future Research and Developments
In the future, research on spironolactone excretion will continue to focus on optimizing drug dosing strategies to enhance its therapeutic effects while minimizing adverse reactions. Novel drug delivery systems may be developed to improve spironolactone excretion and increase patient compliance. Additionally, further studies may explore the potential use of spironolactone in the treatment of other conditions beyond its current indications, such as heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and polycystic ovary syndrome.
